Date
Description of Recent and Upcoming Webinars
Webinar Presentation
03 July 2023
Hong Kong
Decarbonization Opportunities in the Electric Power Sector to Address Climate Change
Keynote Speech, ICEE Conference, Hong Kong
There is an unprecedented level of awareness of climate change and the role of decarbonization in enabling environmental sustainability moving forward. In particular, there has been a major focus placed on the carbon produced through electricity generation, as it is responsible for roughly 30% of emissions globally. While industrialized nations are slowly moving away from fossil-fuel based electricity, emerging economies are still heavily reliant on fossil fuels which are the most readily available electricity generation sources for them.
Thus, there is a tension that needs to be navigated if we are to meet carbon reduction targets – and they are, to be clear, shared targets. A nuanced approach to navigating this tension will see industrialized nation states collaborating with emerging economies to deploy a portfolio of solutions with low-carbon generation, storage and demand side management with advanced technology focusing on energy efficiency. To more efficiently facilitate the global shift towards renewable energy adoption, the below six areas should be our priority to address climate change.
Energy Efficiency Applications
Carbon Capture Systems
Renewable Energy Integration
Hydrogen and Storage Solutions
Cross-Border Energy Transfer
Advanced Nuclear Technologies
Keynote Speech, ICEE, 03 July 2023
Hong Kong
Saifur Rahman, PhD
Joseph Loring Professor & Director
Advanced Research Institute
Virginia Tech, USA
2023 IEEE President & CEO
28 December 2021
Dhaka, Bangladesh
Role of IEEE in Achieving Sustainable Development during 4th Industrial Revolution in Bangladesh
Keynote Speech at the BUET Graduate Club, Dhaka Bangladesh
A smart city relies on widely distributed smart devices to monitor the urban environment in real-time, collects information for intelligent decision making, and facilitates various services to improve the quality of urban living. The distributed network of intelligent sensor nodes, as well as data centers/clouds where sensor data are stored and shared, constitutes a smart city infrastructure. Participatory sensing plays an indispensable role in emerging initiatives of a smart city, which retrieves sensor data from groups of people or communities.
The proliferation of personal mobile devices and development of online social networks make participatory sensing viable at a large scale but introduce many open problems at the same time. Smart cities address urban challenges such as pollution, energy efficiency, security, parking, traffic, transportation, and others by utilizing advanced technologies in data gathering and communications interconnectivity via the Internet. It provides real time and remote monitoring for different aspects of data management in areas such as transportation, communication, video surveillance, and sensors distributed throughout the city. Simultaneously, the Smart City building blocks like education, telemedicine, health care, IT applications, pollution management, etc. can be deployed in Smart Village initiatives to have a greater impact on the rural population throughout the world. This will support the world’s energy-impoverished communities by providing a comprehensive solution combining renewable energy, community-based education, and entrepreneurial opportunities through reliable electricity and internet connectivity.
Webinar IEEE IUT Student Branch
28 Dec 2021
28 December 2021
Gazipur, Bangladesh
The Smart City Building Blocks & Their Synergy with Smart Villages
Islamic University of Technology, Gazipur, Bangladesh
A smart city relies on widely distributed smart devices to monitor the urban environment in real-time, collects information for intelligent decision making, and facilitates various services to improve the quality of urban living. The distributed network of intelligent sensor nodes, as well as data centers/clouds where sensor data are stored and shared, constitutes a smart city infrastructure. Participatory sensing plays an indispensable role in emerging initiatives of a smart city, which retrieves sensor data from groups of people or communities. The proliferation of personal mobile devices and development of online social networks make participatory sensing viable at a large scale but introduce many open problems at the same time. Smart cities address urban challenges such as pollution, energy efficiency, security, parking, traffic, transportation, and others by utilizing advanced technologies in data gathering and communications interconnectivity via the Internet.
It provides real time and remote monitoring for different aspects of data management in areas such as transportation, communication, video surveillance, and sensors distributed throughout the city. Simultaneously, the Smart City building blocks like education, telemedicine, health care, IT applications, pollution management, etc. can be deployed in Smart Village initiatives to have a greater impact on the rural population throughout the world. This will support the world’s energy-impoverished communities by providing a comprehensive solution combining renewable energy, community-based education, and entrepreneurial opportunities through reliable electricity and internet connectivity.
Webinar IEEE IUT Student Branch
28 Dec 2021
23 December 2021
Dhaka, Bangladesh
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Keynote Speech, 8th International Conference on Networking, Systems and Security, Dhaka, Bangladesh
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy.
It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings. The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
22 December 2021
Rajshahi, Bangladesh
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Keynote Speech, International Conference on Electrical & Electronics Engineering, RUET, Rajshahi, Bangladesh
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy.
It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings. The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
17 December 2021
Bangladesh
The Global Electric Power Sector: Engaging with Environmental Issues
Keynote Speech, EICT 2021 KUET, Bangladesh
China, US, India, Japan and Russia are the top five countries in terms of electricity generation capacity. Between them they had a total capacity of 3,650 million kW in 2016. In terms of fuel sources for electricity coal, natural gas, hydro, nuclear, renewables and oil provided 38.3%, 22.9%, 16.3%, 10.2%, 9% and 3.3% respectively in 2017. This means almost two-thirds of the global electricity production came from fossil fuels in that year. This is reflected in about 10 billion tons of CO2 from electricity generation or about a third of the global production.
EICT, KUET Keynote
17-19 Dec 2021
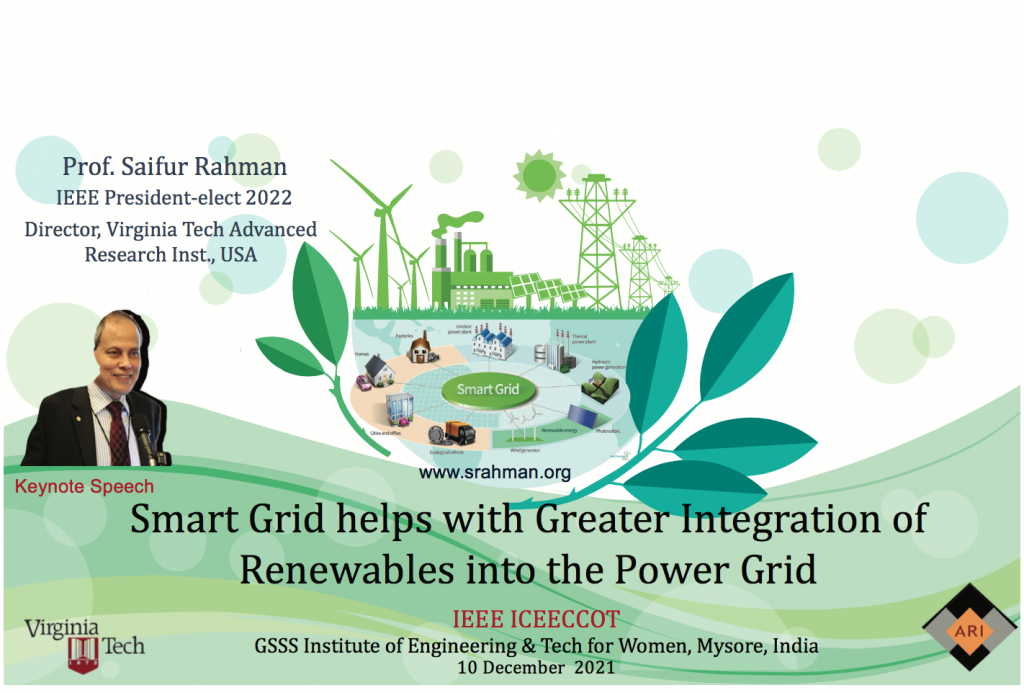
10 December 2021
Mysore, India
Smart Grid Helps with Greater Integration of Renewables into the Power Grid
IEEE ICEECCOT GSSS Institute of Engineering & Tech for Women, Mysore India
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks.
It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation. But in order for this to be possible, the electric utility will have to evolve, and change their ways of operation to become an intelligent provider of these services. This lecture introduces the operational characteristics of renewable energy sources, and various aspects of the smart grid – technology, standards and regulations. It also addresses the interplay among distributed generation, storage and conventional generation to provide an efficient operational strategy in the context of the smart grid.
IEEE ICEECCOT
10-11 Dec 2021
27 November 2021
Maryland, USA
The Electric Power Secto in Bangladesh: Global Decarbonization Issues
35th FOBANA and AABEA Joint Seminar
The electric power sector in Bangladesh is expected to grow very fast – system peak is expected to reach 16,823 MW in 2021, then 37,024 MW in 2030 and 72,379 MW in 2041. This level of load growth will require generation, transmission and distribution support. Given the limited national expertise available, there is strong dependence on manufacturers’ reps who push for their products and consultants who are busy writing their reports. This cycle needs to be broken.
Technical challenges facing the electric power sector include: over-capacity in generation, lack of a North-South transmission corridor, lack of distribution automation, poor reliability of power supply, and challenges of renewables integration.
Possible Solution approaches include:
- Change the way the power system is operated by developing a different work ethic which makes key players take ownership of the situation.
- This needs resources and trained manpower who can think differently.
- If short term targets are not met, reasons must be found and remedies applied.
- There needs to be a paradigm shift in the way the power system is maintained and operated in the country.
- Interconnections with neighboring countries needed to take advantage of diversity.
AABEA-FOBANA presentation
27-28 Nov 2021
26 November 2021
Morocco
The Smart City Building Blocks & Their Synergy with Smart Villages
International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Humanity 2021
A smart city relies on widely distributed smart devices to monitor the urban environment in real-time, collects information for intelligent decision making, and facilitates various services to improve the quality of urban living. The distributed network of intelligent sensor nodes, as well as data centers/clouds where sensor data are stored and shared, constitutes a smart city infrastructure. Participatory sensing plays an indispensable role in emerging initiatives of a smart city, which retrieves sensor data from groups of people or communities. The proliferation of personal mobile devices and development of online social networks make participatory sensing viable at a large scale but introduce many open problems at the same time.
Smart cities address urban challenges such as pollution, energy efficiency, security, parking, traffic, transportation, and others by utilizing advanced technologies in data gathering and communications interconnectivity via the Internet. It provides real time and remote monitoring for different aspects of data management in areas such as transportation, communication, video surveillance, and sensors distributed throughout the city. Simultaneously, the Smart City building blocks like education, telemedicine, health care, IT applications, pollution management, etc. can be deployed in Smart Village initiatives to have a greater impact on the rural population throughout the world. This will support the world’s energy-impoverished communities by providing a comprehensive solution combining renewable energy, community-based education, and entrepreneurial opportunities through reliable electricity and internet connectivity.
Keynote Speech
ICATH, Rabat, Morocco
26 November 2021
25 November 2021
South Africa
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Invited Talk, University of Johannesburg, South Africa
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation.
In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks. It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation. But in order for this to be possible, the electric utility will have to evolve, and change their ways of operation to become an intelligent provider of these services. This lecture introduces the operational characteristics of renewable energy sources, and various aspects of the smart grid – technology, standards and regulations. It also addresses the interplay among distributed generation, storage and conventional generation to provide an efficient operational strategy in the context of the smart grid.
24 November 2021
Qatar
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Keynote Speech, International Conference on Sustainable Energy-Water-Environment Nexus in Desert Climates
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks. It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation.
23 November 2021
Morocco
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Keynote Speech, 9th International Renewable and Sustainable Energy Conference
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks. It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation.
But in order for this to be possible, the electric utility will have to evolve, and change their ways of operation to become an intelligent provider of these services. This lecture introduces the operational characteristics of renewable energy sources, and various aspects of the smart grid – technology, standards and regulations. It also addresses the interplay among distributed generation, storage and conventional generation to provide an efficient operational strategy in the context of the smart grid.
Keynote Speech, IRSEC’21, Morocco
17 November 2021
Indonesia
The Smart City Building Blocks & Their Synergy with Smart Villages
ASEAN Distinguished Lecture, IEEE PES Indonesia and ASEAN Engineering Inspectorate
A smart city relies on widely distributed smart devices to monitor the urban environment in real-time, collects information for intelligent decision making, and facilitates various services to improve the quality of urban living. The distributed network of intelligent sensor nodes, as well as data centers/clouds where sensor data are stored and shared, constitutes a smart city infrastructure. Participatory sensing plays an indispensable role in emerging initiatives of a smart city, which retrieves sensor data from groups of people or communities. The proliferation of personal mobile devices and development of online social networks make participatory sensing viable at a large scale but introduce many open problems at the same time. Smart cities address urban challenges such as pollution, energy efficiency, security, parking, traffic, transportation, and others by utilizing advanced technologies in data gathering and communications interconnectivity via the Internet.
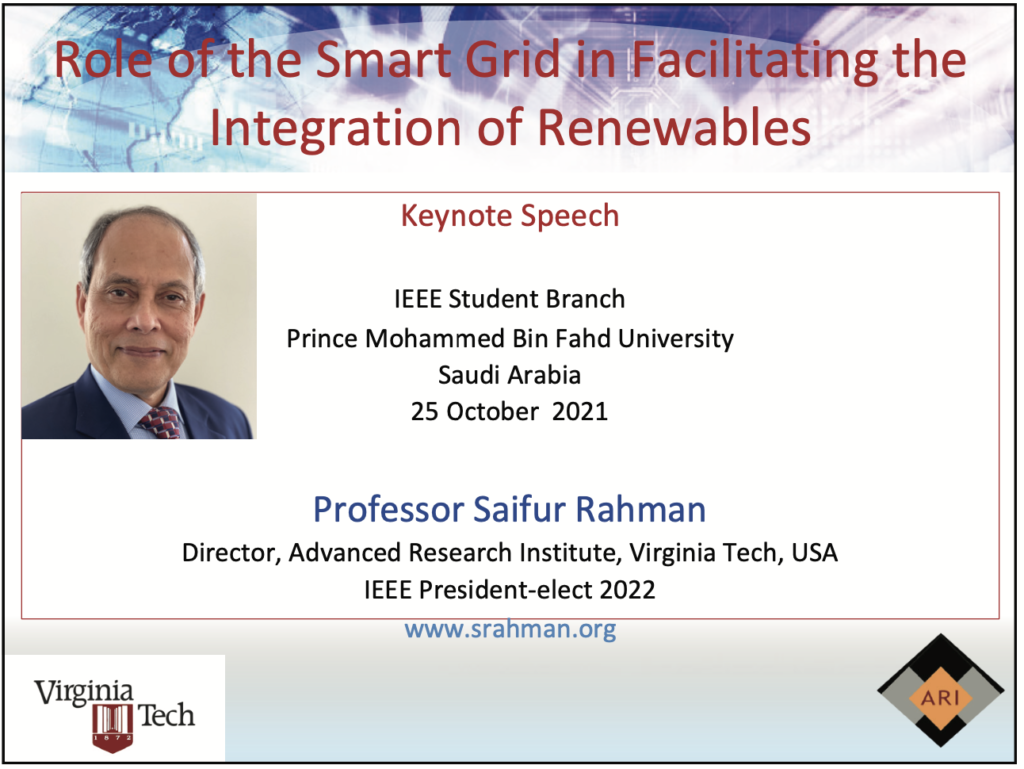
18 October 2021
Calicut, India
The Smart City Building Blocks & Their Synergy with Smart Villages
Invited Talk, Faculty Development Program, Dayalbagh Educational Institute, Agra, UP
A smart city relies on widely distributed smart devices to monitor the urban environment in real-time, collects information for intelligent decision making, and facilitates various services to improve the quality of urban living. The distributed network of intelligent sensor nodes, as well as data centers/clouds where sensor data are stored and shared, constitutes a smart city infrastructure. Participatory sensing plays an indispensable role in emerging initiatives of a smart city, which retrieves sensor data from groups of people or communities. The proliferation of personal mobile devices and development of online social networks make participatory sensing viable at a large scale but introduce many open problems at the same time.
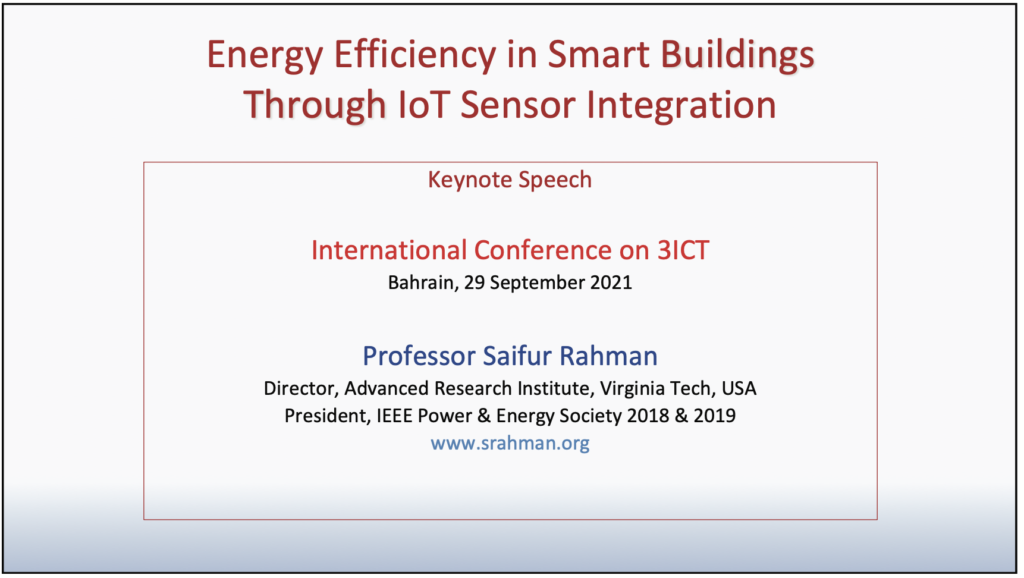
29 September 2021
Bahrain
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Keynote Speech, International conference on 3ICT
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy. It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings.
The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
17 July 2021
USA
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Invited Speech, IEEE Consumer Technology Society Webinar
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy. It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings.
The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
12 August 2021
Canada
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Keynote Speech, 2021 IEEE 9th International Conference on Smart Energy Grid Engineering, Ontario Canada
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks. It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation.
05 August 2021
Dhaka
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
International Conference on Science and Contemporary Technologies, Bangladesh University of Business and Technologies
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks. It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation.
19 July 2021
Kerala, India
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Keynote Speech, St. Joseph College of Engineering and Technology, Kerala India
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy. It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings.
The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
11 July 2021
Bangalore
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Keynote Speech, IEEE Connect, Bangalore
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks. It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation.
06 July 2021
Agra, UP, India
The Smart City Building Blocks & Their Synergy with Smart Villages
Faculty Development Program, Dayalbagh Educational Institute, Agra, UP
A smart city relies on widely distributed smart devices to monitor the urban environment in real-time, collects information for intelligent decision making, and facilitates various services to improve the quality of urban living. The distributed network of intelligent sensor nodes, as well as data centers/clouds where sensor data are stored and shared, constitutes a smart city infrastructure. Participatory sensing plays an indispensable role in emerging initiatives of a smart city, which retrieves sensor data from groups of people or communities. The proliferation of personal mobile devices and development of online social networks make participatory sensing viable at a large scale but introduce many open problems at the same time.
01 July 2021
Kerala, India
AI and Machine Learning in System Load Forecasting Research
Keynote Speech, International Conference on Smart Comp and Comm.
Forecasting is important in traffic volume management, optimum loading of mobile phone networks, managing electric power networks and managing building environmental control as a function of building occupancy levels. If we focus on the electric power system, we observe that the system operation is getting more and more complex due to the following reasons: more electrification means more demand which needs more reliable electricity requiring more efficient supply with less available margins. On top of this, the increased use of renewables causes system integration challenges. The research community needs new tools for dealing with uncertainty where artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) can be used to supplement human intelligence. Artificial intelligence enables computers and machines to mimic the perception, learning, problem-solving, and decision-making capabilities of the human mind. These issues are highlighted in this presentation.
30 June 2021
Kolkata, India
The Smart City Building Blocks & Their Synergy with Smart Villages
Invited Talk, Amity University Kolkata, Webinar
A smart city relies on widely distributed smart devices to monitor the urban environment in real-time, collects information for intelligent decision making, and facilitates various services to improve the quality of urban living. The distributed network of intelligent sensor nodes, as well as data centers/clouds where sensor data are stored and shared, constitutes a smart city infrastructure. Participatory sensing plays an indispensable role in emerging initiatives of a smart city, which retrieves sensor data from groups of people or communities. The proliferation of personal mobile devices and development of online social networks make participatory sensing viable at a large scale but introduce many open problems at the same time.
17 June 2021
Kerala, India
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Keynote Speech, ICCISc, GEC Idduki, Kerala, India
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy. It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings.
The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
15 June 2021
Brazil
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Invited Talk, IEEE PES South Brazil Chapter
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks. It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation.
13 June 2021
Bangladesh
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Be Researcher BD Forum, Bangladesh
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy. It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings.
The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR
10 June 2021
Morocco
Opportunities and Challenges for Digital Transformation
of City Services
Smart City Casablanca Symposium
A smart city relies on widely distributed smart devices to monitor the urban environment in real-time, collects information for intelligent decision making, and facilitates various services to improve the quality of urban living. The distributed network of intelligent sensor nodes, as well as data centers/clouds where sensor data are stored and shared, constitutes a smart city infrastructure. Smart cities address urban challenges such as pollution, energy efficiency, security, parking, traffic, transportation, and others by utilizing advanced technologies in data gathering and communications interconnectivity via the Internet. It provides real time and remote monitoring for different aspects of data management in areas such as transportation, communication, video surveillance, and sensors distributed throughout the city. Simultaneously, the Smart City building blocks like education, telemedicine, health care, IT applications, pollution management, etc. can raise challenges of interdependency, reliability and resilience which citizens need to be aware of and be expected to deal with.
07 June 2021
Saudi Arabia
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Keynote Speech, SUM
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks.
26 April 2021
Malaysia
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Invited Speech, IEEE UKM Student Branch
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks.
It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation. But in order for this to be possible, the electric utility will have to evolve, and change their ways of operation to become an intelligent provider of these services. This lecture introduces the operational characteristics of renewable energy sources, and various aspects of the smart grid – technology, standards and regulations. It also addresses the interplay among distributed generation, storage and conventional generation to provide an efficient operational strategy in the context of the smart grid.
22 April 2021
Morocco
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Invited Speech, IEEE PES EMI Student Branch Chapter
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks.
It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation. But in order for this to be possible, the electric utility will have to evolve, and change their ways of operation to become an intelligent provider of these services. This lecture introduces the operational characteristics of renewable energy sources, and various aspects of the smart grid – technology, standards and regulations. It also addresses the interplay among distributed generation, storage and conventional generation to provide an efficient operational strategy in the context of the smart grid.
12 April 2021
Mauritius
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Invited Talk, IEEE Mauritius Section
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy.
It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings. The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
19 February 2021
USA
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
AEI-EI Distinguished Lecture, ASEAN
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy.
It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings. The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
12 February 2021
USA
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
ICMDCS Conference, VIT, Vellore, India
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy.
It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings. The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
04 February 2021
UAE
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Keynote Speech at ICREGTConference, UAE University
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks.
It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation. But in order for this to be possible, the electric utility will have to evolve, and change their ways of operation to become an intelligent provider of these services. This lecture introduces the operational characteristics of renewable energy sources, and various aspects of the smart grid – technology, standards and regulations. It also addresses the interplay among distributed generation, storage and conventional generation to provide an efficient operational strategy in the context of the smart grid.
03 February 2021
USA
Energy Efficiency in Smart Buildings through IoT Sensor Integration
Invited Talk, IEEE Electron Devices Society
Internet of Things (IoT) deployments offer a much higher value proposition if these can function in the context of smart buildings. Such advanced information and communication technology (ICT) applications in commercial buildings, schools, libraries, shopping centers, etc. offer low cost but highly effective monitoring and control opportunities. Sensors deployed in key locations can monitor the building environment in real-time, collect information for intelligent decision making, and facilitate various services. An IoT sensor platform has been developed that provides a unified communication platform which can integrate information from disparate sources and provide one control hierarchy.
It is a powerful, low-cost, open-architecture software platform that can monitor and control major electrical loads (e.g., HVAC, lighting and plug loads), as well as solar PV systems, energy storage units and other IoT sensors in commercial buildings. The platform can provide new or legacy buildings with a building automation system (BAS) or connect with existing BAS systems in large and small commercial buildings. This platform leverages machine learning algorithms to draw insights from a deployed building’s historical operating data and occupant preferences to save energy (kWh) while increasing occupant comfort. This also allows buildings to reduce peak demand (kW) through direct communication with utilities using demand response protocols such as openADR.
28 January 2021
Georgia Tech, USA
How to Write an Effective Technical Paper
Invited Talk, IEEE PES Student Chapter
In this presentation Prof. Saifur Rahman will highlight issues with paper structure, conference vs. journal papers, ethics, where to publish, open access, impact factor, etc. He will also highlight the IEEE publications business, the value and quality of IEEE publications, and the broad topical areas IEEE publications cover.
21 January 2021
Shanghai, China
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
Invited Lecture at Shanghai Jiaotong University
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks.
It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation. But in order for this to be possible, the electric utility will have to evolve, and change their ways of operation to become an intelligent provider of these services. This lecture introduces the operational characteristics of renewable energy sources, and various aspects of the smart grid – technology, standards and regulations. It also addresses the interplay among distributed generation, storage and conventional generation to provide an efficient operational strategy in the context of the smart grid.
20 January 2021
Iran
Role of the Smart Grid in Facilitating the Integration of Renewables
IEEE Iran Section and the University of Kurdistan
With the focus on environmental sustainability and energy security, power system planners are looking at renewable energy as supplements and alternatives. But such generation sources have their own challenges – primarily intermittency. It is expected that the smart grid – due to its inherent communication, sensing and control capabilities – will have the ability to manage the load, storage and generation assets (including renewables) in the power grid to enable a large-scale integration of distributed generation. In a smart grid, information about the state of the grid and its components can be exchanged quickly over long distances and complex networks.
It will therefore be possible to have the integration of sustainable energy sources, such as wind, solar, off-shore electricity, etc. for smoother system operation. But in order for this to be possible, the electric utility will have to evolve, and change their ways of operation to become an intelligent provider of these services. This lecture introduces the operational characteristics of renewable energy sources, and various aspects of the smart grid – technology, standards and regulations. It also addresses the interplay among distributed generation, storage and conventional generation to provide an efficient operational strategy in the context of the smart grid.
Date
Description of Recent and Upcoming Webinars
Webinar Presentation
Date
Description of Recent and Upcoming Webinars
Webinar Presentation